The Intelligent Pantry: How Hotel Kitchens Are Leveraging AI
Globally, hotel kitchens are leveraging AI to enhance sustainability, reduce waste, and foster culinary innovation. In India, a few hotels and restaurants have begun to explore this technology, though the cultural emphasis continues to favour personal touch.
By Deepali Nandwani
Think of a kitchen that blends the genius of Artificial Intelligence (AI here onward) and the creativity of a fantastic chef. AI is no longer a futuristic fantasy; it's rapidly becoming a cornerstone of modern professional kitchens in restaurants and hotels across the globe. The technology will reshape how these culinary spaces operate in the future, as hotels and restaurants struggle with managing food wastage and promoting sustainability.
At the core of this revolution lies AI's capacity to reshape fundamental kitchen operations. Imagine the rhythmic precision of robotic arms deftly chopping vegetables, or intelligent systems artfully plating dishes with an unwavering consistency that speaks of automation. AI-powered robots and smart appliances are stepping into roles that once demanded countless human hours, equipped with an array of sensors, cameras, and sophisticated machine learning algorithms. These systems don't just perform tasks; they learn and adapt, meticulously monitoring cooking processes to ensure quality and consistency previously unattainable. This automation naturally translates to a significant reduction in labour costs, freeing up human chefs to focus on the more creative and nuanced aspects of their craft.
AI helps deal with the perennial challenge of inventory management and food wastage, as these intelligent systems act as astute forecasters, analysing a wealth of data—from past sales figures and reservation patterns to the subtle ebbs and flows of historical consumption trends. By discerning these patterns, AI can accurately predict future stock requirements, effectively minimising the occurrence of overstocking and the subsequent waste of precious ingredients. This proactive approach not only makes sound economic sense but also aligns perfectly with the growing need for adopting sustainable practices.
Across the globe, innovative establishments are already leveraging the power of AI to redefine their kitchen operations.
At Hilton Hotels in the United Arab Emirates, artificial intelligence is playing a transformative role in tackling food waste, particularly at breakfast buffets. The group has adopted Winnow Vision, an AI-powered system with motion-sensor cameras and scales, to meticulously monitor discarded food items. This technology identifies commonly wasted items such as bread, pastries, and eggs, and generates actionable data that chefs use to fine-tune portion sizes and adjust menu offerings accordingly.
In 2023, Hilton piloted a ‘Green Breakfast’ initiative across 13 UAE properties. Over four months, the results were striking: pre-consumer (kitchen) waste was reduced by 76%, and post-consumer (plate) waste dropped by 55%. These transformations were achieved through thoughtful changes such as offering smaller croissants, pre-cut fruits, and scaled-down portions of salmon.
Hilton’s focus on waste reduction is rooted in leveraging AI-generated insights to help culinary teams avoid over-preparation and enhance the presentation and portioning of buffet items—two key contributors to the high levels of waste typically associated with buffet service.
Globally, Accor Hotels has embarked on a multi-pronged AI strategy through partnerships with startups such as Winnow Vision, Orbisk, and Fullsoon. Each platform contributes uniquely: Winnow Vision scans and quantifies food waste, Orbisk analyses leftovers to guide menu changes, and Fullsoon forecasts customer demand and ingredient needs. These technologies have delivered measurable results across Accor properties.
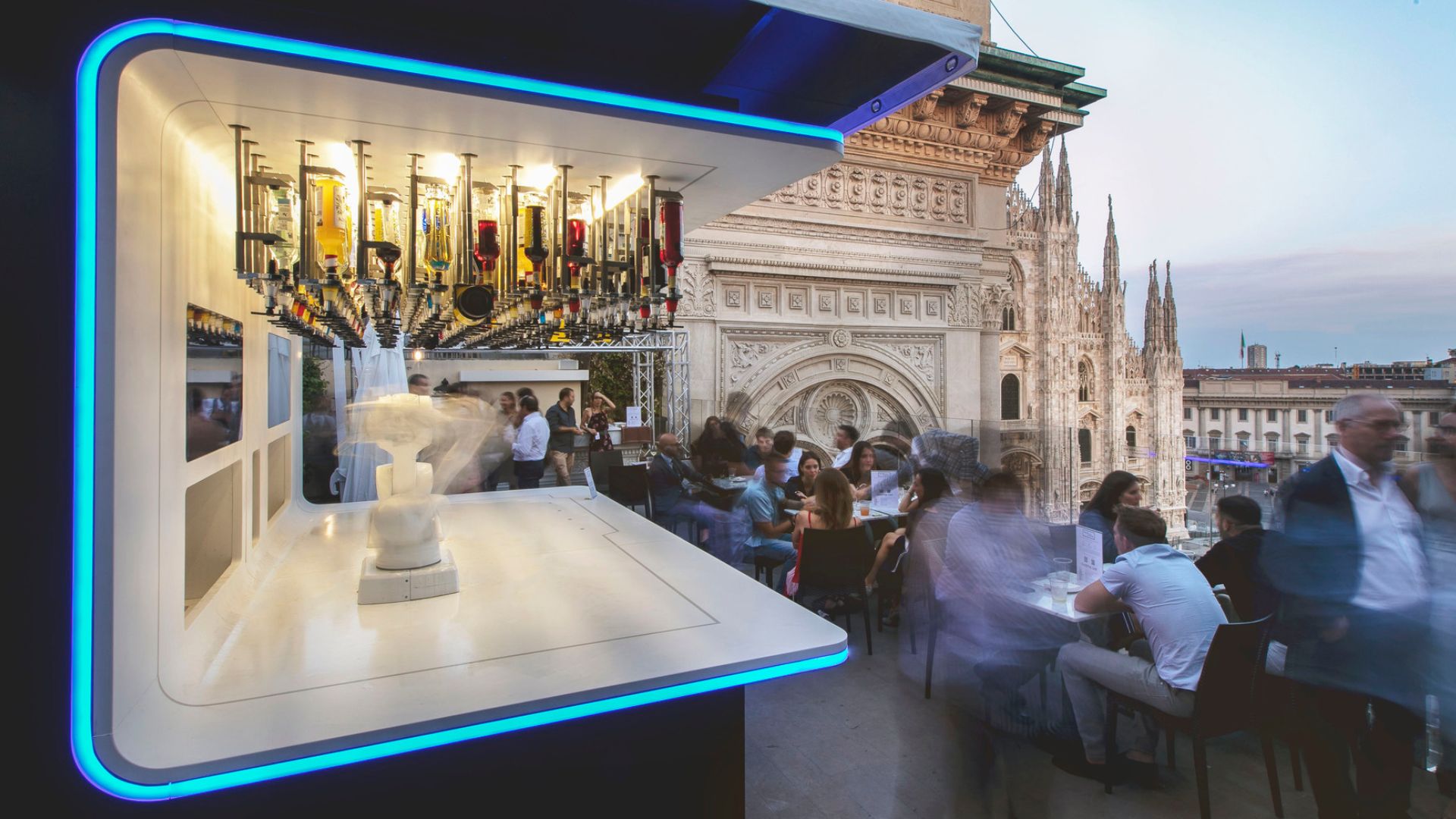

An automated bar dispenser.
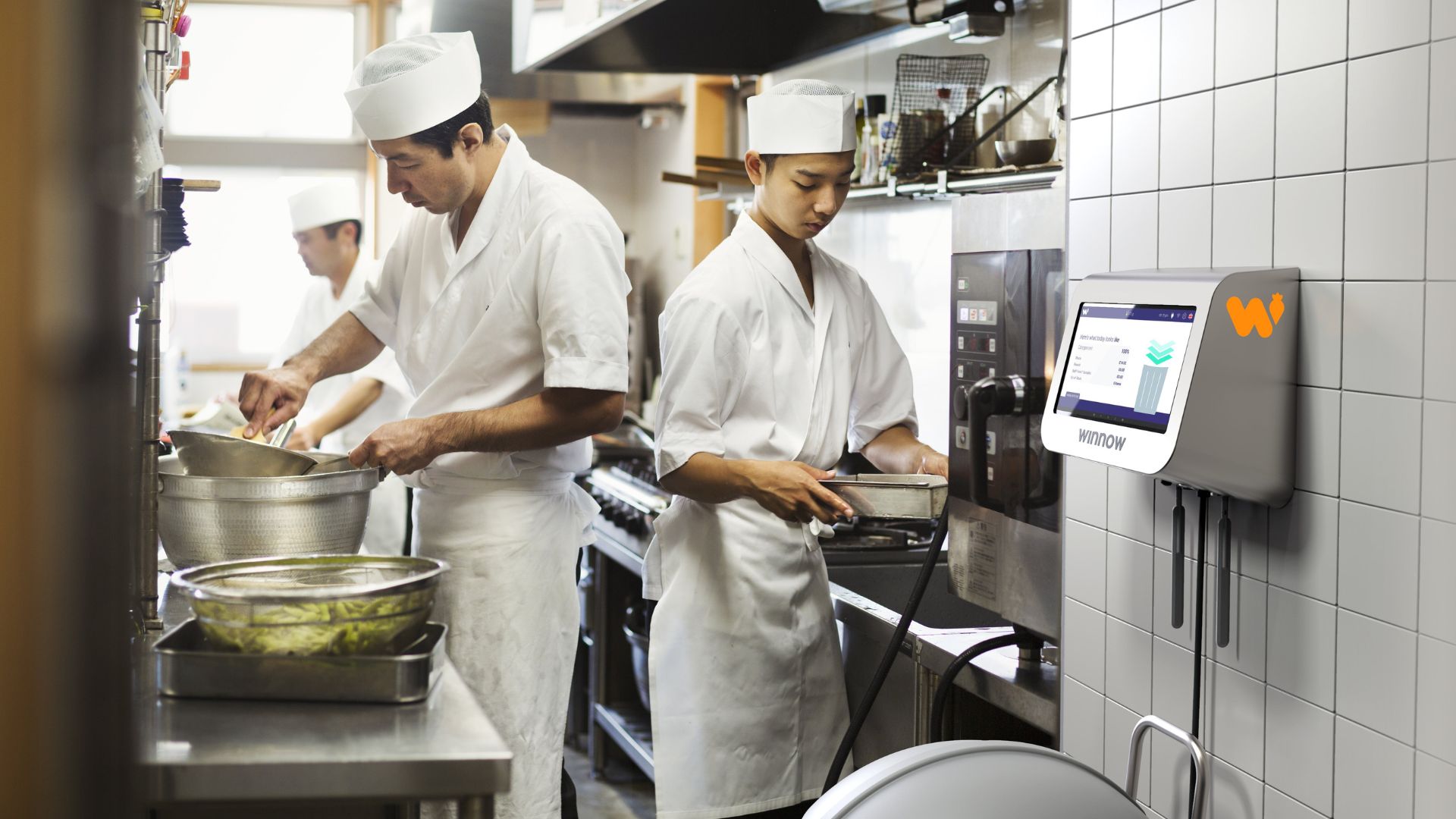

Winnow Vision's AI-powered system is employed by several hotel chains
to monitor discarded food items.
At Fairmont Jakarta, food waste dropped by 16% (1.6 tons) in a year. Novotel London Excel achieved a 39% reduction (12 tons), Sofitel The Palm Dubai cut waste by 13% (3 tons annually) in five months, and Novotel Amsterdam Schiphol Airport recorded a 35% drop (8 tons over two years). In collaboration with Too Good To Go, Accor also saved 137 tons of uneaten food in 2023 through redistribution. The chain uses its Gaïa reporting tool and AI-generated data to guide procurement and menu planning, to halve food waste by 2030.
The Iberostar Group, operating over 100 hotels globally, also relies on Winnow’s AI to combat food waste. By integrating cameras and scales to monitor food disposal, the system generates data that informs menu optimisation and purchasing decisions. Since January 2023, Iberostar has saved 735,000 meals and reduced waste by 11%, the equivalent of 1,264 tons of CO₂. With an annual target of saving 1,600 tons of food, the initiative also projects over $7 million in cost savings. The group aimed for a 50% reduction in food waste within the first year and a goal of sending zero waste to landfill by this year.
InterContinental Hotels Group (IHG), which spans Europe, the Middle East, Asia, and Africa, has partnered with Winnow Solutions as well to deploy its Winnow Vision technology. The system collects data from food preparation and plate returns, helping chefs and managers make informed decisions about inventory and menus. At InterContinental Fujairah Resort in the UAE, food waste dropped by over 50% in just six months. Seven IHG hotels in the EMEAA region currently use this technology, with another 30 properties in the pipeline. IHG has set a target of reducing food waste by 30% across its portfolio.
In the Middle East, Emaar Hospitality Group, which operates 12 properties, uses Winnow Vision to identify and quantify discarded food. Kitchen teams receive AI-driven insights to help streamline operations. This approach has yielded a 72% reduction in food waste and approximately $350,000 in savings in a relatively short period. These efforts not only align with customer expectations but also support government sustainability mandates.
While some hotels focus on minimising food waste, others are using AI to explore the creative frontier of food innovation. At Grand Mercure Mysore in India, AI is used to personalise menus based on guests' dietary needs and preferences. The hotel also employs 3D food printing for customised desserts and garnishes, and uses smart ovens like Rational’s Self Cooking Centre, which leverage AI for consistent cooking results. The hotel grows herbs and vegetables through vertical farming, reducing its supply chain footprint. These innovations not only cater to diverse tastes, especially for banquets, but also help control portions and ingredient usage.
In Las Vegas, The Cosmopolitan has deployed an AI chatbot named Rose to offer personalised dining recommendations to guests based on their preferences and past interactions. Behind the scenes, kitchen AI systems analyse guest data to experiment with new menu items and optimise food preparation. This data-driven experimentation aligns menu offerings with demand, reducing waste and boosting guest satisfaction by highlighting trending dishes.
The Dorchester Collection, with properties in the UK and beyond, applies machine learning to comb through guest reviews across digital platforms. Insights from these reviews have revealed preferences such as customised breakfast offerings, prompting new menu directions. AI also supports chefs experimenting with novel flavour combinations, ensuring new creations align with guest expectations. This approach streamlines production by focusing on high-demand items and minimising ingredient waste.
At Henn-na Hotel in Japan—known for its robotic staff—AI takes on an even more futuristic role. The hotel uses AI for automated food preparation and delivery, deploying kitchen assistants and robotic couriers. Data analytics inform menu experimentation, ensuring only the most popular dishes are scaled for broader service. This model reduces labour costs and waste through precision portioning while offering guests a high-tech dining experience.
Key trends emerge across these varied efforts. Hotels such as Hilton, Accor, Iberostar, IHG, Emaar, and TUI Blue are focused on waste reduction through AI platforms like Winnow Vision and KITRO. These tools enable real-time tracking, menu optimisation, and inventory management, leading to food waste reductions ranging from 13% to 76%. On the other hand, properties such as Grand Mercure Mysore, The Cosmopolitan, Dorchester Collection, and Henn-na Hotel use AI to explore food personalisation, automation, and 3D printing—creating memorable guest experiences while keeping waste in check.
These strategies are often tied to ambitious sustainability goals, such as Iberostar’s target of zero landfill waste by this year and Accor’s commitment to halving waste by 2030. Despite challenges such as upfront investment and the need for staff training, major hotel chains are proving the scalability and effectiveness of AI systems across diverse properties.
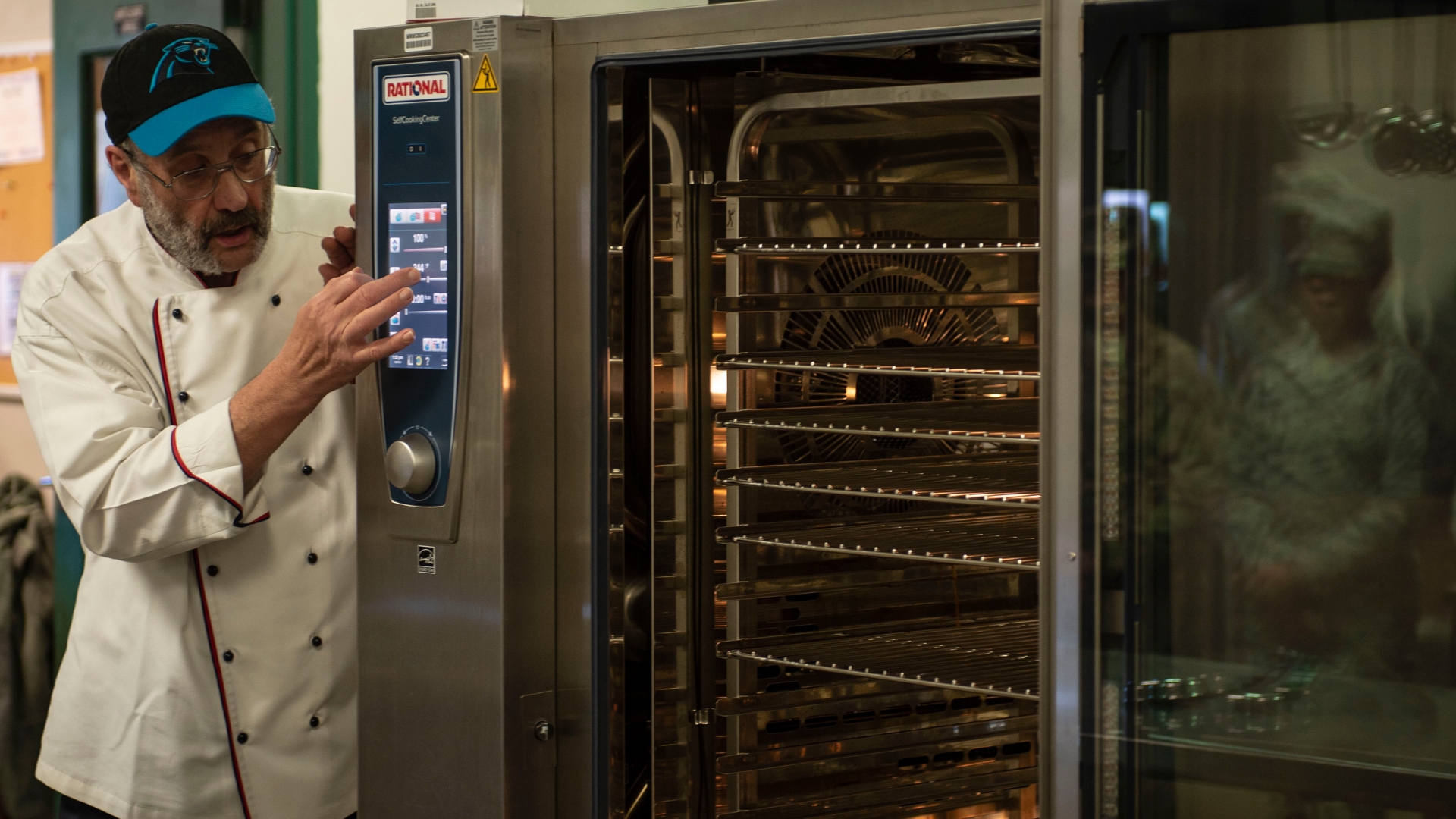

Smart ovens such as Rational cook with precision, negating the need for intensive human intervention.

AI can free up humans for creative tasks.
While some hotels focus on minimising food waste, others are using AI to explore the creative frontier of food innovation.

Why is Indian hospitality still on a slow adaptation route?
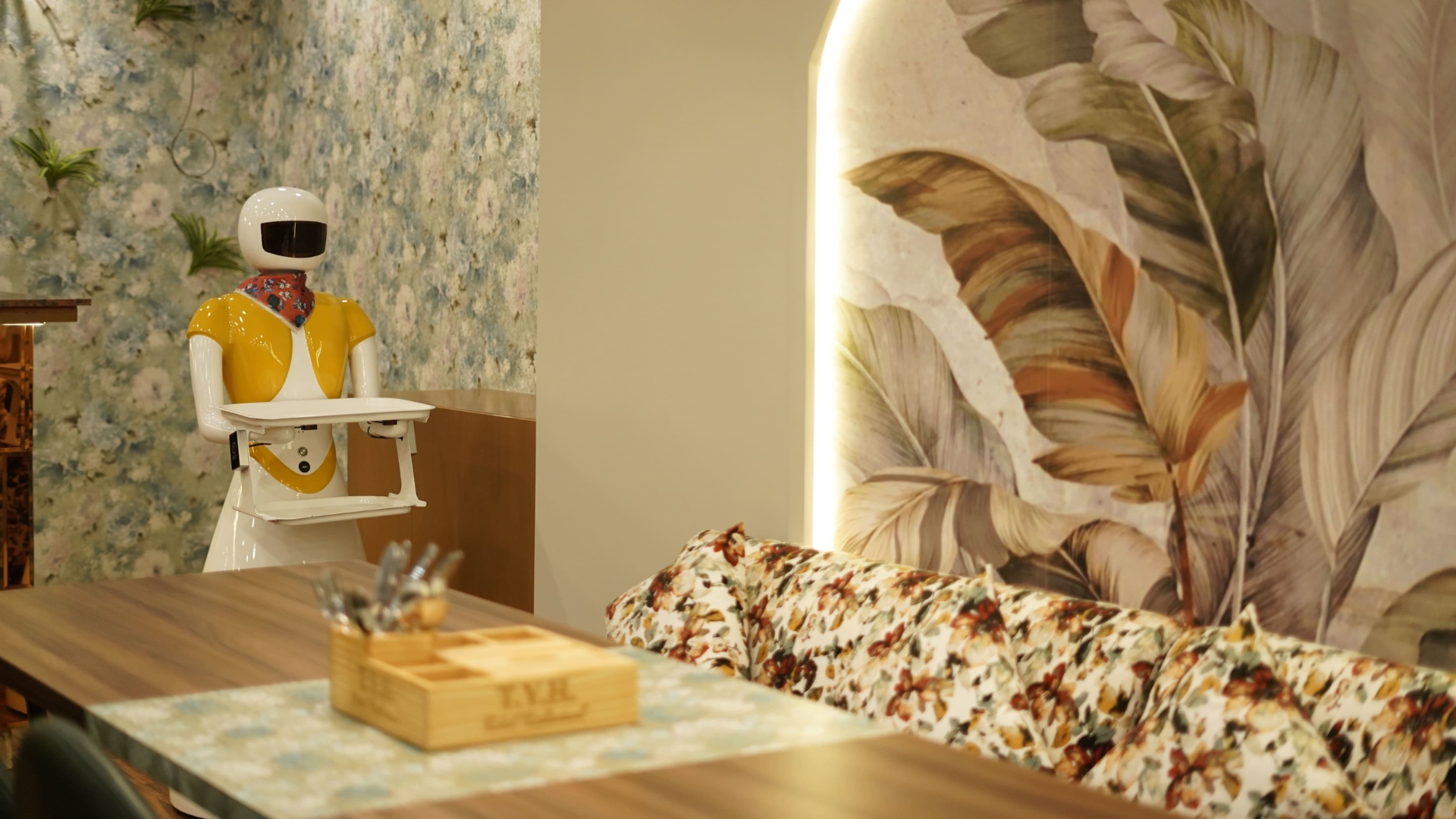
AI-driven innovation in Indian luxury hotels is focused on menu personalisation and enhancing guest engagement. The Yellow House, a robot restaurant in Jaipur, offers a unique dining experience with AI-powered robotic servers named Ruby and Diva. While human staff handle order taking, these robots efficiently deliver food to tables, seamlessly integrating table data. This novel approach attracts customers, reduces service time, and addresses labour shortages, although human chefs remain essential for preparing the diverse range of Indian dishes.
The Bombay Canteen in Mumbai has tangentially utilised AI to enhance the dining ambience. For their ‘Raja Ravi Varma’s Feast of Wonders’ Onam event, they employed AI-generated art to create an immersive experience. Additionally, AI chatbots assist with menu planning and customer engagement, demonstrating how technology can elevate the overall dining experience, even while chefs emphasise the irreplaceable cultural and emotional significance of human cooking.
Full-scale kitchen automation, however, is progressing more cautiously due to the deep-rooted cultural appreciation for the haath ka swad—the unique flavour imparted by the human touch. Restaurants such as The Second House in Goa use AI for their design needs, but keep it out of their kitchen. The restaurant does have an AI device in the kitchen in the form of the Rational oven, which cooks exactly to the same precision every time, without chefs having to monitor the temperature or the cooking.
Besides cultural moorings, the high cost of AI-integrated appliances (ranging between ₹70,000 and ₹1,80,000) acts as a huge deterrent to the large-scale adoption of the technology.
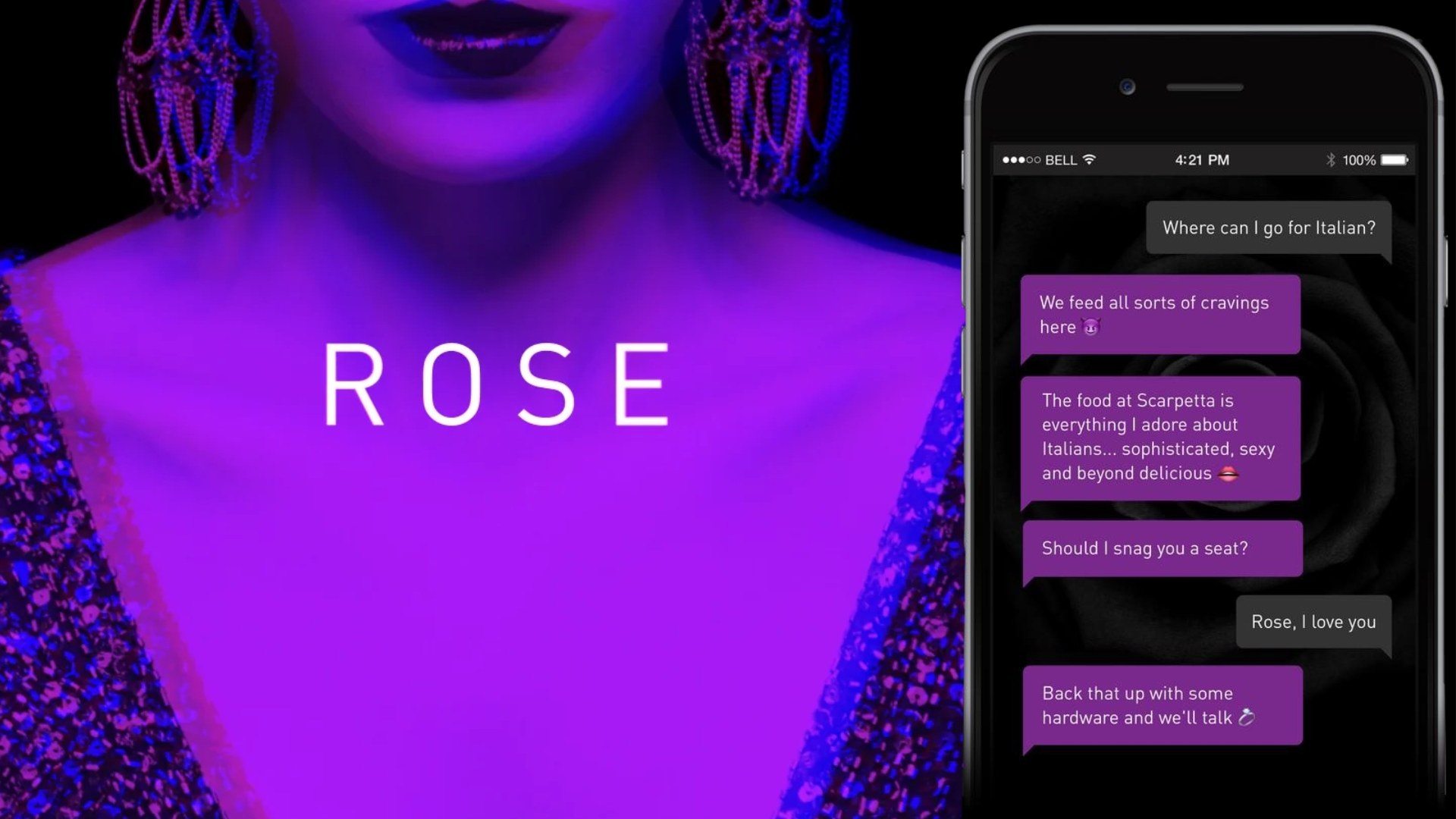
The Cosmopolitan, Las Vegas, has a chatbot named Rose to offer personal dining recommendations.

At Fairmont Jakarta, food waste dropped after Accor Hotels embarked on a multi-pronged AI-led strategy; A 3D printed dessert.
AI-driven innovation in Indian luxury hotels is focused on menu personalisation and enhancing guest engagement.

Research insights: quantifying the impact
Research studies are beginning to quantify the growing influence of AI in professional kitchens:
Food Waste Reduction: Research by Chen Wang, an assistant professor at University of Buffalo and an AI specialist, highlights the significant role of AI in reducing food waste within European hotels, with similar applications gaining traction in India, as evidenced by Winnow's implementation at Marriott.
Labour Impact: Gartner, a global company that provides research, advisory, consulting and peer services to help businesses make faster, smarter decisions and achieve stronger performance, predicts that AI could potentially replace 10% of call centre workers by 2026. But the perception in professional kitchens is that AI will serve as a valuable complement to human creativity rather than a direct replacement for chefs.
Sustainability: The role of AI in promoting sustainability is gaining momentum, with tools like Winnow and the integration of vertical farming practices, as seen at Grand Mercure Mysore, effectively reducing waste and carbon footprints. AI is reshaping the way hotels manage food, both as a resource to conserve and as a canvas for creativity. From cutting waste in buffet lines to personalising fine dining, the technology is driving a new era of sustainability and innovation in hospitality. The industry is setting a precedent for how intelligent systems can support environmental responsibility and elevated guest experiences.
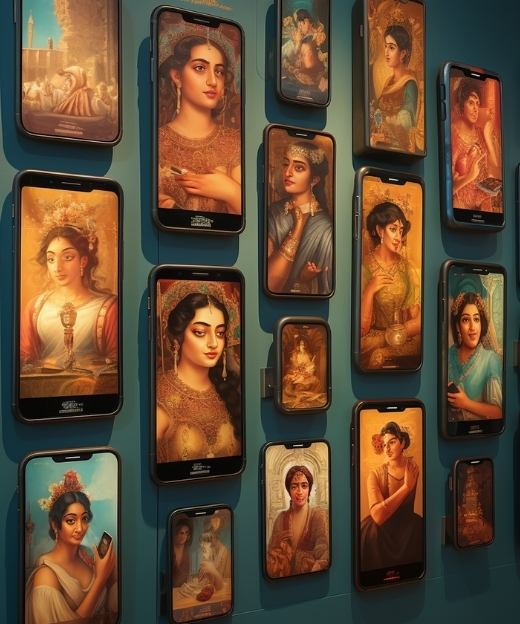

For their ‘Raja Ravi Varma’s Feast of Wonders' Onam event, The Bombay Canteen employed AI-generated art to create an immersive experience.
Research by Chen Wang, an assistant professor at University of Buffalo and an AI specialist, highlights the significant role of AI in reducing food waste within European hotels, with similar applications gaining traction in India, as evidenced by Winnow's implementation at Marriott.

Looking ahead: future trends in AI for kitchens
The future of AI in professional kitchens promises even more exciting developments:
Generative AI: Advanced language models are poised to enhance multilingual support and create highly personalised dining guides, as seen in emerging applications within the hospitality sector.
Sensory AI: Companies are actively developing AI-based smell detectors, which could potentially enable AI to assess food quality in a more holistic manner within the next two to three years.
Sustainability Focus: AI will continue to drive eco-friendly practices, such as the increased adoption of on-site vertical farming and sophisticated waste reduction strategies, aligning with growing consumer demand for sustainable dining options.
AI is streamlining operations through automation, minimising waste, enabling personalised menus, and fostering sustainability. As AI continues its evolution, it is likely to complement rather than replace the artistry of chefs, ushering in an era where technology and culinary tradition converge to create the kitchens of the future.
































